1. Totten Glacier
In Climate clippings 124 I mentioned concerns about Totten Glacier in East Antarctica, which is actively melting. It’s now in the news again. Dr Tas van Ommen:
“We’re realising that the East Antarctic ice sheet’s probably not the sleeping giant that we thought or at least, the giant’s starting to twitch and we’re concerned,” he said.
This article has a map showing the size of the glacier catchment, more than double Victoria:
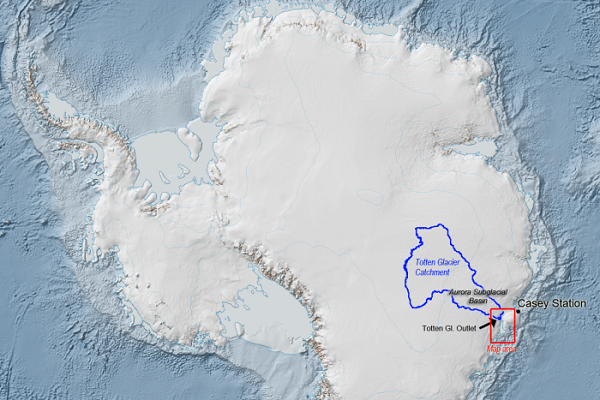
Essentially with East Antarctica on the move, estimations of sea level rise this century could be underdone. We simply don’t know.
2. Great Barrier Reef ‘saved’
The Federal and Queensland Governments have together released the final version of the long-term plan for the Great Barrier Reef.
The Reef 2050 Long-Term Sustainability Plan satisfies one of the key recommendations made by the United Nation’s World Heritage Committee and forms a key plank in the Governments’ bid to avoid the site being declared “in danger” by UNESCO.
The report warns climate change is the biggest long-term threat facing the reef, while the immediate pressures include water quality, which has declined due to nutrient and sediment runoff from agricultural production.
Previously, a draft version of the report was criticised by some scientists as being a plan for sustainable development rather than protecting and conserving the reef.
The Queensland Government also sought urgent changes to the draft, to include its $100 million election commitment to improve water quality.
These news items never mention ocean acidification. As I’ve repeatedly warned:
It has been shown that “preserving more than 10 per cent of coral reefs worldwide would require limiting warming to below +1.5°C (atmosphere–ocean general circulation models (AOGCMs) range: 1.3–1.8°C) relative to pre-industrial levels”.
3. France says new rooftops must go green
According to a new French law approved on Thursday, rooftops on new buildings in commercial zones across France must either be partially covered in plants or solar panels.
France has lagged behind other major European countries like Germany, Italy and Spain in solar power development. As of last summer, France had just over five gigawatts of photovoltaic capacity, accounting for around one percent of total energy consumption. Germany has nearly 40 GWs installed.
France has relied on nukes for 83% of its power.
4. Are the UK’s emissions really falling?
Traditional emissions accounting only considers the greenhouse gases generated within a country’s own borders. In other words, emissions produced in the UK are allocated to the UK. On this measure, UK emissions have fallen dramatically to around 25% below 1990 levels.
But when the source of emissions generated by products consumed within the UK are counted, emissions have only fallen by 7%. This is the pattern over time:
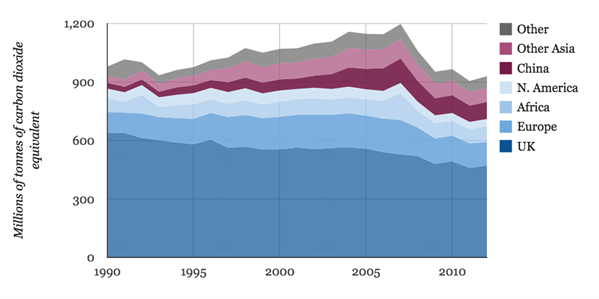
The UK’s production emissions have fallen fast (dark blue area), but imports have offset much of the gain (lighter blues, purples and grey area). Clearly things changed after the GFC in 2008.
5. Germany penalises dirty coal power
Germany plans to force operators of coal plants to curb production at their oldest and most-polluting power stations, as part of efforts to achieve its climate targets, senior government sources said yesterday. Under the measures, the government plans to allow coal plants to produce 7 million tonnes of carbon dioxide per gigawatt of installed capacity, but any produced above that level would be subject to a fine of 18 to 20 euros per ton.
6. Australia’s top ten emitters
Planet Oz takes a look at an ACF report on Australia’s top polluting companies. From the report here they are:
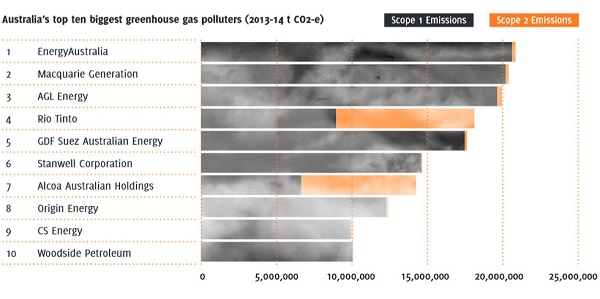
Seven are energy companies, three are miners.
However, if you took the emissions generated from the products they produce, a very different picture would emerge. Rio, for example comes fourth with emissions of 18 million tonnes of CO2 last year. Yet Rio’s customers burning coal produce a further 129 million tonnes.
7. Climate change ‘exacerbated’ Cyclone Pam damage
That’s according to the Climate Council, (but see Item 8 below).
“Higher surface temperatures can mean that you have higher wind speed and more damaging rainfall,” Amanda McKenzie from the Council said.
“And what we saw in Vanuatu was in the lead-up to the cyclone, sea surface temperatures were well above average.”
Ms McKenzie said rising sea levels would multiply the damaging effects of cyclone storm surges.
Cyclone Pam, a category-5 storm with wind gusts reaching 300 km/h, struck Vanuatu on 13 March 2015 leaving twenty-four people dead, 100,000 people homeless and up to 70% of the nation’s 69,000 households damaged.
8. Cyclone Pam and Climate Change
Stefan Rahmstorf at RealClimate takes a look at whether climate change had an effect on Cyclone Pam.
My take is, quite possibly, but we can’t know for sure.
The basic problem is that the satellite record only goes back to around 1980, which is not long enough, and only in the North Atlantic are cyclones surveyed by aircraft and then only if they threaten populated regions within a few days.
A study by Kossin et al (2013) looked at the satellite data record from 1982 to 2009 and found an increase of 2.5 m/s per decade for high intensity events (Pam appears to have reached an intensity of around 75 m/s).
Other factors to look out for include the amount of rain delivered, changes in genesis locations and tracks, and diameters, all of which should be affected by climate change.
Haiyan and Pam, two of the most severe tropical cyclones on record, have struck the western Pacific in the past 16 months.



 Recently we took a look at the most recent coral bleaching event in
Recently we took a look at the most recent coral bleaching event in 



