This edition is somewhat themed around climate policy and planning in China, the US and Australia. It also includes items on puffins in Maine, the Lowy Institute poll and the warm weather we’ve been having in May.
1. Petey Puffin dies on camera

Puffins were once common on the coast off Maine but were eliminated by overhunting. In recent years there has been a project to repopulate the area, which was proceeding well accompanied by a cam project where children around the world could watch the birds in their habitat. Petey Puffin, a chick being fed by its parents became a popular focus. The only problem was that the parent birds kept bringing him butterfish which were just too large for him to swallow. This went on day after day until the chick died on camera.
The project co-ordinator then checked the 64 other burrows being monitored to find that only 30% of chicks survived.
Problem was that hake and herring normally abundant around Maine had moved north as the water warmed to be replaced by butterfish.
The warmer water brought many other changes to the waters off Maine.
Incidents such as these remind people that they are living in the midst of climate change.

2. President Obama gets serious on climate change
From John Abraham at Climate Consensus – the 97%:
President Obama just announced a major effort to reduce global-warming gases from United States power plants. These new rules, and his prior strong actions on climate change, signify a major shift for the United States. No longer is the U.S. the world laggard on dealing with climate change – we are quickly becoming the leader.
We finally have a president that understands science. We finally have a president that honestly includes scientists as decision makers – rather than effectively muzzle them. We finally have a president that recognizes the social and economic costs of climate change. We finally have a president who is charting a pathway that may lead us to bend the curve of emissions downward so that the most serious climate change consequences are avoided.
Most importantly, we finally have a president who is a world leader.
3. Not everyone is happy
John Podesta before rejoining the White House inner circle in an interview said history will not applaud the measures taken by Obama as it fails to meet what the science demands. It won’t limit us to a 2°C temperature rise, and 2°C is too dangerous.
A 30% reduction by 2030 from 2005 levels shrinks to 7.7% if you use the international baseline of 1990. Moreover, coal will be replaced by gas, where the ‘fugitive’ methane emissions are not counted.
Podesta says that in Obama’s first term his top aides never took climate change seriously. Ironically, Podesta as Obama’s transition director in 2008 helped select those aides.
4. China to cap emission
China will seek to cap fossil fuel emissions for the first time, we are told.
Reading carefully it seems that emissions will still grow, but not as fast as business as usual.
Pointing out that there are 1.6 billion people in the US and China, Amanda McKenzie CEO of Climate Council thinks the decisions are a game changer.
5. Time for Tony Abbott to admit his climate policy is crap
In case you missed it, that is Giles Parkinson’s advice to Abbott.
Parkinson says Australia should be embarrassed by its lack of action compared to the United States and China, which has indicated it will place a cap on its emissions as soon as 2016.
Ironically, Abbott could have a pretty good collection of climate and renewable energy policies just by doing nothing. Everything Labor put in place is still there, apart from Tim Flannery and the Climate Commission, which has morphed into the Climate Council with private money and public donations.
6. Lowy poll
The Lowy Institute Poll 2014 is now available.
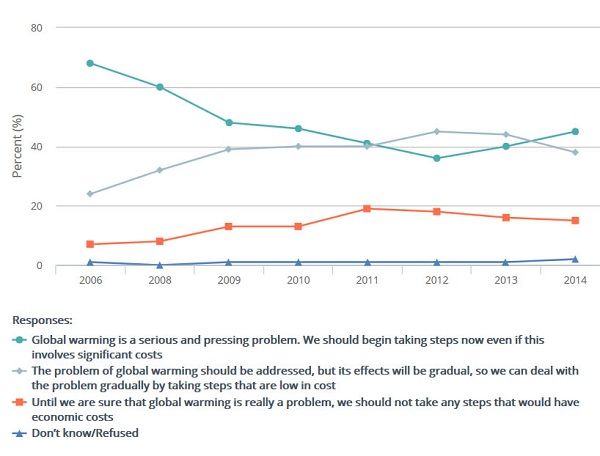
The number of Australians now saying global warming is a “serious and pressing problem” and that “we should begin taking steps now even if this involves significant costs” is now 45%.
Some 38% now say the the problem of global warming should be addressed, but its effects will be gradual, so we can deal with the problem gradually by taking steps that are low in cost. 15% think we should leave it until we are sure it’s a problem if costs are involved. Here’s the graph:
63% of people thought the government should be taking a leadership role in reducing emissions.
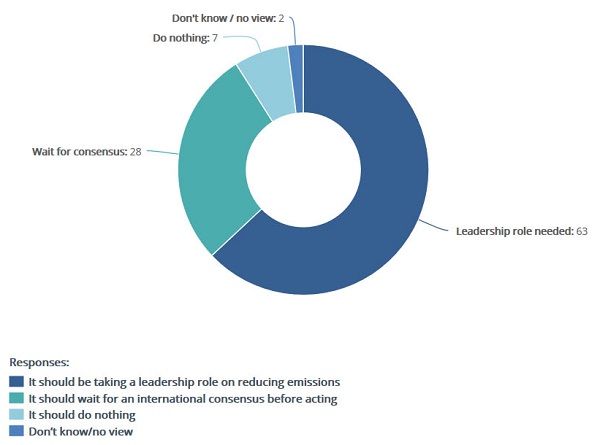
I guess Abbott would claim that’s what they are doing.
7. Heat wave in May
Will Steffen talks here and here about the unusually warm period in May, which I believe officially rates as a heat wave.
A remarkable, prolonged warm spell occurred over the period 8-26 May, with daytime temperatures 4 to 6°C above normal over much of south-central Australia, extending from South Australia and northwest Victoria into Queensland and the Northern Territory.
The Scientific American noticed.
BOM think we are in for a warm winter:
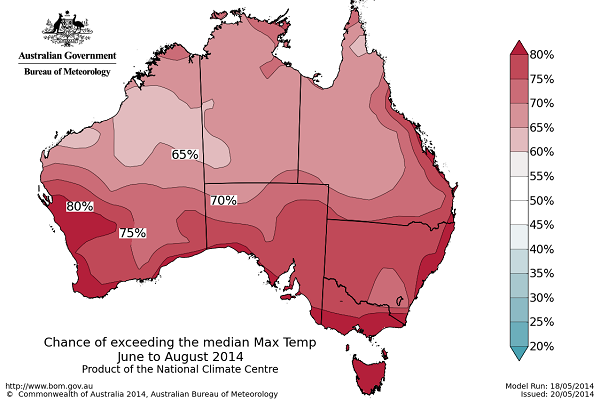
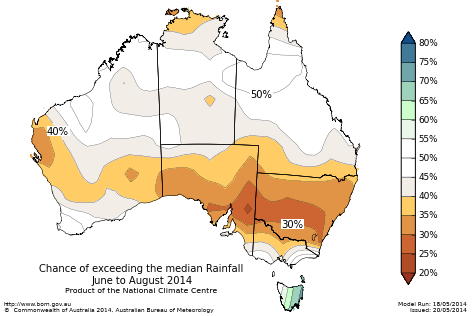
And drier for large parts of the southern mainland:
Reminder: Use this thread as an open thread on climate change.


 Recently my wife and I saw an item on the TV about the
Recently my wife and I saw an item on the TV about the 



