1. Abbott adviser warns of threat of ‘global cooling’
Nevertheless with the certainty only possessed by fools, the Abbott government’s chief business adviser, Maurice Newman, has warned that Australia is ill prepared for global cooling owing to widespread “warming propaganda” in his latest critique of mainstream climate science.
The suggestion is that temperature change is due to changes in solar activity, cosmic rays and stuff. The science is heading in the opposite direction.
“The sun doesn’t have as much influence on the climate as we previously thought, the latest estimates are that it explains only 5% of the warming over the last 150 years,” he said.
How can the government be advised by someone who is so ill-informed about arguably the biggest single influence on business conditions over the next century.
2. August hottest ever
We’ve just had the hottest August globally since records began being kept in 1880, according to NASA. The year to date has been the fourth hottest on record. Hot years usually coincide with an El Niño either in the year concerned or the previous year. An El Niño has not yet arrived but does look likely according to the latest information.
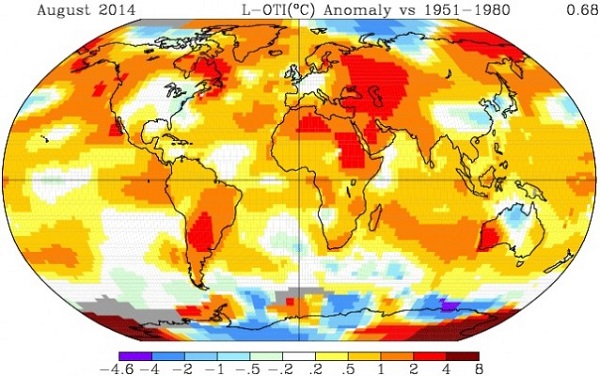
It has been especially hot in West Antarctica. Bear that in mind when you see stories of record sea ice around Antarctica:
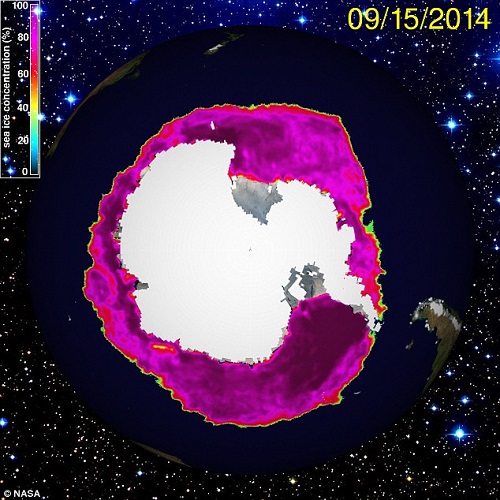
This is not incompatible with global warming and could in fact be caused by it. Melting ice produces cold water, and the tightening wind pattern tend to blow the ice further north.
There is no information as yet on ice volume.
3. Australian Climate Action Summit 2014
The Australian Climate Action Summit 2014 is on this weekend. Since my life is governed by work, the weather and medical appointments I am unable to go.
On Sunday there will be a People’s Climate March, organised by an outfit called Avaaz. Marches will be organised all around the world, and indeed, all around Australia, including, for example Mt Isa and the Gold Coast. If you click on Brisbane you get the Summit, but if you click on the Summit you don’t get a march. So if there is a march in Brisbane, I can guess where but I’d also need to guess when.
The march is meant to impress the leaders gathering in New York on Tuesday 23 September. That’s the UN Summit Tony Abbott will not attend although he’ll be in New York on Wednesday.
4. Surviving in hot, acidic oceans
I think this is a good news story.
More than 90% of the extra heat in global warming ends up in the oceans, as does 25% of the CO2 we create, which makes the oceans more acidic. Shell-making organisms such as plankton are expected to be in trouble. The good news is that it seems one species of plankton, the Emiliania huxleyi, can survive the changes underway.
5. Climate Council report on sea level
The Climate Council has taken another look at climate change and coastal flooding. The focus is on 1.1 metres sea level rise by 2100, all too possible if West Antarctica is in play, as it seems to be.
We are told that the frequency of flooding events can treble for every 10 cm of sea level rise. The risk multiplier depends where you are. In Sydney, Bundaberg and Hobart, for example a current 1 in 100 year event now could be happening every day by 2100. In Adelaide, the least at risk city, it would be only once every year.
At risk we have $87 billion worth of commercial and light industrial buildings, $72 billion worth of homes and $67 billion worth of roads and rail infrastructure.
6. Capitalism v The Climate
Joe Romm tells us about Naomi Klein’s new book, This Changes Everything: Capitalism Vs. The Climate. Klein, he says, makes three essential points:
1. Because we have ignored the increasingly urgent warnings and pleas for action from climate scientists for a quarter century (!) now, the incremental or evolutionary paths to avert catastrophic global warming that we might have been able to take in the past are closed to us.
2. Humanity faces a stark choice as a result: The end of civilization as we know it or the end of capitalism as we know it.
3. Choosing “unregulated capitalism” over human civilization would be a “morally monstrous” choice — and so the winning message for the climate movement is a moral one.
The time for ‘evolutionary’ strategies is long past. Now only ‘revolutionary’ strategies will get us there. Unregulated capitalism is a Ponzi scheme, which must collapse. The real choice facing us is a moral one.
Unchecked capitalism is immoral and will destroy civilisation as we know it. Just what Klein says we should do will be covered by Romm in a subsequent post.