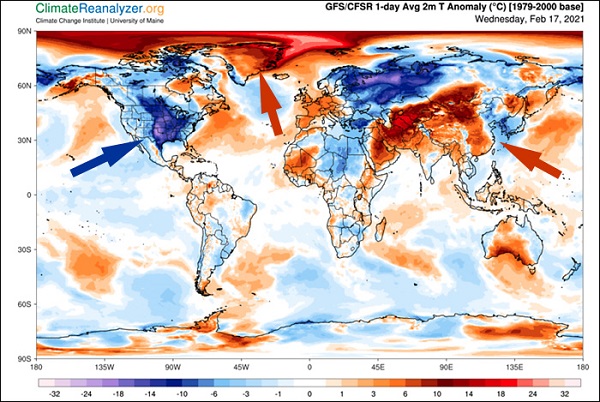
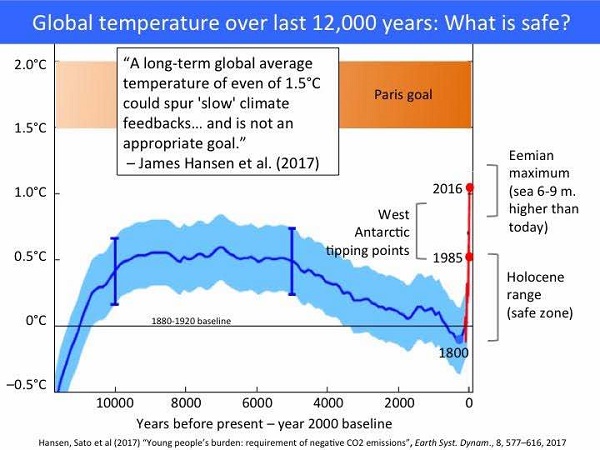
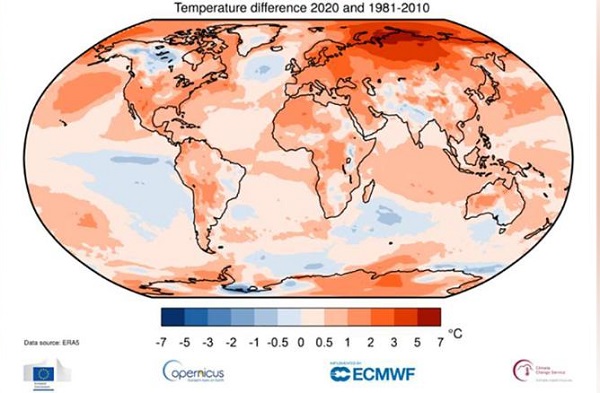
In January this year when David Spratt took a look at whether tipping points had already been passed for critical climate systems he found that coral reefs were in death spiral. From reef ecology scientists:
-
“The time between recurrent events is increasingly too short to allow a full recovery of mature coral assemblages, which generally takes from 10 to 15 years for the fastest growing species and far longer for the full complement of life histories and morphologies of older assemblages.”
Mass bleaching occurred in 1998, 2002, 2016, 2017 and 2020. Continue reading Farewelling the Great Barrier Reef