I like to think that at Climate Plus we cover all the important issues and happenings. In this edition we look at two significant reports, one by Jeffrey Sachs to the UN Secretary General and the IEA’s World Energy Investment Outlook 2014.
As usual use Climate clippings as an open thread on climate change.
1. Deep Decarbonization Pathways
Renowned economist Jeffrey Sachs found that Australia could cut emissions from its energy sector to zero by 2050 and still grow GDP by an average of 2.4% over that period. That was in an interim report recently delivered to UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon plotting
specific measures for the world’s 15 largest economies, including China, India and the US, to cut their emissions quickly and deeply enough to meet an international agreed goal of limiting warming to two degrees above pre-industrial levels.
What we do matters!
The report
found that it’s technically possible for Australia to get almost all of its electricity from renewable sources by 2050 and to offset the rest by storing carbon in soil or planting more trees.
We can do that while GDP grows at 2.4% per annum, but it is interesting that our per capita growth rate is the lowest of the 15, India the highest.
There’s more about Sachs here.
2. Catalyst does sea level rise
It was scary, but could have, should have been scarier.
The program depended heavily on the last interglacial, the Eemian, as an analogue for now. It made the link through temperatures and probably got them a bit wrong. We’ll likely get more than 2°C this century, and the Eemian global average was possibly only 1°C higher than now.
Fundamentally the problem is this. CO2 levels during the Eemian which produced around 9 metres of sea level rise were never above 300 ppm. At 400 ppm, as we are now, the implied sea level rise is more like 20 to 25 metres, played out over the centuries.
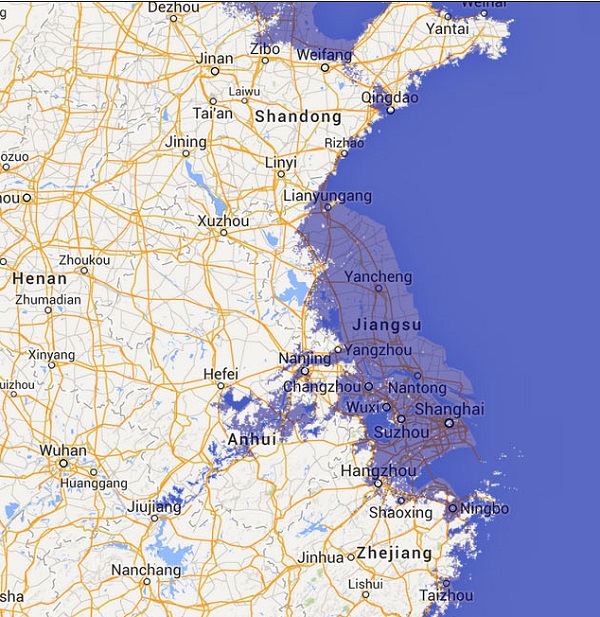
Still they could have pointed out just how horrendous a 9 metre rise would be, other than the throwaway comment about most mega cities being displaced. At 9 metres significant chunks disappear from continents as in China:
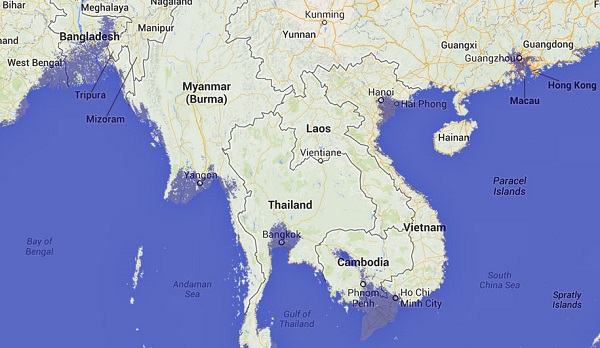
Here’s SE Asia courtesy of the Firetree flood map:
At the end it suggested that we could cope by building sea walls, except that it would be expensive. Sea walls are not going to cope with nine metres, let alone 20.
This Skeptical Science post gives useful information about the Eemian, although it too arguably needs updating. I think scientists are settling on a higher sea level rise for the Eemian than the 5 metres suggested, more like the 9 metres of the Catalyst program. Also at least some parts of Greenland are thought to have been 10°C warmer than now, rather than 5°C.
3. The search for the clean coal holy grail
Radio National’s generally excellent Background Briefing program has turned its guns on a ‘clean coal’ technology called DICE – Direct Injection Carbon Engine. Would you believe, a DICE engine runs on a slurry of finely ground coal and water? One purpose seems to be to make brown coal as emissions efficient as black coal – a pointless exercise in terms of current climate mitigation needs. Inherently significant energy must be spent to get the coal into the required state.
The history seems to be one of shonky technology projects run by shonks, but the CSIRO is now involved and our visionary government is throwing money at the venture.
4. World Energy Investment Outlook 2014
The International Energy Association’s latest report is billed as its first full update since the 2003 World Energy Investment Outlook. It’s been out since 3 June. So far I’ve failed in my ambition to do a separate post, so I’ll just do a brief note here.
This post from the Post Carbon Institute is a packet of joy. It says that the IEA report “should send policy makers screaming and running for the exits” or looking for early retirement. Seems we need a mere $48 trillion in investment through to 2035 to keep things on track. But:
The IEA forecasts that only 15 percent of the needed $48 trillion will go to renewable energy. All the rest is required just to patch up our current oil-coal-gas energy system so that it doesn’t run into the ditch for lack of fuel. But how much investment would be required if climate change were to be seriously addressed? Most estimates look only at electricity (that is, they gloss over the pivotal and problematic transportation sector) and ignore the question of energy returned on energy invested. Even when we artificially simplify the problem this way, $7.2 trillion spread out over twenty years simply doesn’t cut it. One researcher estimates that investments will have to ramp up to $1.5 to $2.5 trillion per year. In effect, the IEA is telling us that we don’t have what it takes to sustain our current energy regime, and we’re not likely to invest enough to switch to a different one.
If you look at the trends cited and ignore misleading explicit price forecasts, the IEA’s implicit message is clear: continued oil price stability looks problematic. And with fossil fuel prices high and volatile, governments will likely find it even more difficult to devote increasingly scarce investment capital toward the development of renewable energy capacity. (Emphasis added)











 These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as a roundtable. Again, I do not want to spend time in comments rehashing whether human activity causes climate change.
These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as a roundtable. Again, I do not want to spend time in comments rehashing whether human activity causes climate change.


