This post started out as four related items in Climate clippings. When a fifth showed up I decided to extract them and put them in a separate post. Hence it is a collection of opinions and perspectives rather than an analysis of the future of coal as such. Still, a message seems to emerge.
BHP calls for carbon pricing
Believe it or not Andrew Mackenzie, CEO of BHP Billiton, has called for a price to be put on greenhouse gas emissions to address the threat of global warming.
Talking in Houston Texas on the future of fossil fuels and carbon emissions Andrew Mackenzie said BHP needs to think carefully about controlling its carbon emissions. He wants BHP to lead the way. BHP is the world’s largest mining company and the third biggest company in the world.
Beyond coal the company is also a major player in shale gas in the USA, investing a cool $US20 billion in 2012.
Mackenzie was on message about ‘clean coal’, spruiking the virtues of carbon capture and storage (CCS).
Rio weighs in
Rio Tinto’s head of energy, Harry Kenyon-Slaney, also weighed in saying “Idealistic discussions” about climate change should be abandoned and Australians should recognise that coal will remain an important energy source for decades.
Coal will continue to “do the lion’s share of heavy lifting” to meet energy demand, he says.
Rio has invested $100 million in carbon capture and storage.
Martin Ferguson, now an adviser to the Australian Petroleum Production & Exploration Association:
stepped up criticism of the Coalition government’s emissions-reductions policies and called for the watering down of the renewable energy target, which he said was undermining the national electricity market.
Tristan Edis comments
Tristan Edis comments on Rio Tinto’s clean coal idealism.
He reckons CCS would be great if you could also retrofit it to existing coal-fired power stations, implement it at large scale and a reasonable cost and start doing it by, say, 2025.
The Australian Coal Association instituted an industry-funded initiative to progress zero-emission coal with a levy and created ACA Low Emissions Technology Ltd (ACALET) to undertake initiatives. Unfortunately from 2012-13 the requirement to pay the levy was suspended and ACALET is now concentrating on promoting the use of coal in Australia and overseas.
Edis reports that Industry Minister Ian Macfarlane seems to be willing to acknowledge that carbon capture and storage is a pipedream.
One senior Liberal referred to it as ‘vaporware’ (new computer software promised by companies to be delivered in the future that never eventuates but scares off competing software development).
The end of coal?
Paul Gilding has called the end of coal and the dawn of renewables, especially solar.
He believes the fossil fuel industry live in a delusionary analytical bubble, convinced of their own immortality. They are about to be swept away. Markets can be brutal.
The top 20 European utilities have lost $600 billion in value over the past 5 years.
Tesla, presumably because it makes electric vehicles (see also below), is now worth more than half GM although GM makes 300 times as many cars.
HSBC’s Global Solar index rose 65% last year and is already up 23% in 2014.
Underground coal gasification
Trials are underway or planned in diverse parts of the world in burning in situ coal that can’t be mined, according to an article by Fred Pearce in the New Scientist (paywalled). The process is underground coal gasification (UCG).
The potential is enormous, with enough coal available to supply the world with energy for 1000 years. For example, 70% of the coal in the UK has never been mined. One company has a licence to prospect for UCG sites beneath more than 400 square kilometres of the North Sea.
The attraction of UCG is not just power production. The process produces methane, carbon monoxide, hydrogen as well as CO2. The Brits see potential to use these chemicals as feedstock to revitalize their industrial chemicals industry. The article lists the following uses:
- Gas to electricity Power stations can burn methane to produce electricity for the grid
- Gas to chemicals Hydrogen, methane and CO all have value as feedstock for the chemicals industry
- Gas to liquid Methane can be liquefied (LNG) for storage or transport, or the CO and hydrogen converted through the Fischer-Tropsch process to synthetic diesel fuel for vehicles
- Gas to tech Hydrogen can provide an alternative transport fuel
CO2 can be reinjected into the void created by the burnt coal.
The article refers to a 2007 MIT study which found that commercial CCS was unlikely before 2030. Undaunted Myles Allen, an Oxford University climate scientist, reckons that CCS is the “only practical way forward”.
Christiana Figueres is hopeful
Christiana Figueres, Executive Secretary of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), points to 60 countries with 500 pieces of climate legislation, and is confident that an international climate change agreement will be delivered on time in 2015. She looks forward within 20 years to the time where everything new we do will be carbon neutral.
She does see a need for research into energy storage – batteries – and into CCS.
It is only with marketable CCS that we will be able to use the fossil fuels that we need. Storage and CCS would be my top two choices for technology investment.
If so someone, for example BHP and Rio, get cracking.
Meanwhile…
Meanwhile
Investment bank Morgan Stanley says it has been overwhelmed by the response to its recent analysis which suggested that the falling costs of both solar modules and battery storage presented a potential tipping point that would encourage huge numbers of homeowners and businesses in the US to go off grid.
And Tesla is building a $5 billion ‘gigafactory’ for battery production, then providing an
emergency power service by monitoring the power levels in home batteries and delivering replacement batteries in the event home batteries run out of power.
Someone should tell Andrew Mackenzie and Harry Kenyon-Slaney they’ll need to shake a leg with CCS. Schumpeter’s creative destruction seems to be at work in the energy industry.
Update: Murray Energy, the largest independent coal producer in the US, is suing the EPA for not taking into account job losses when formulating emissions regulations.







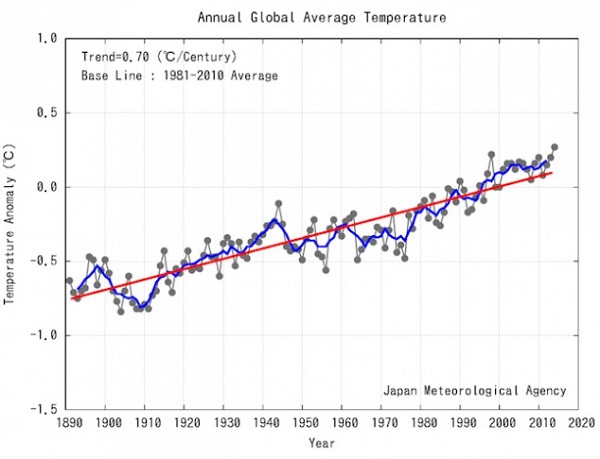



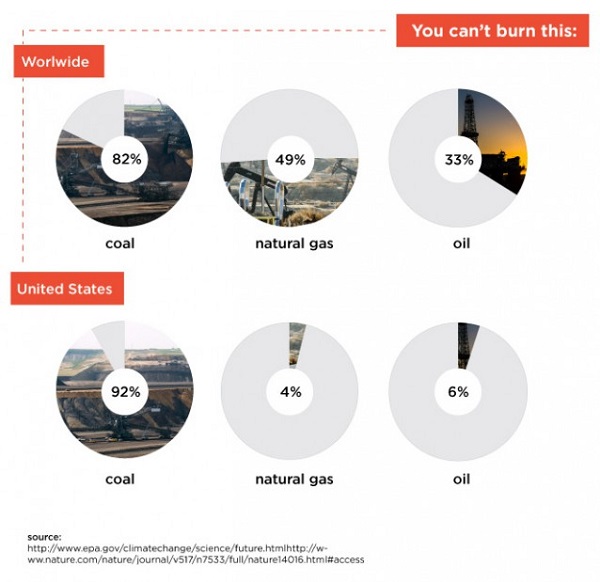
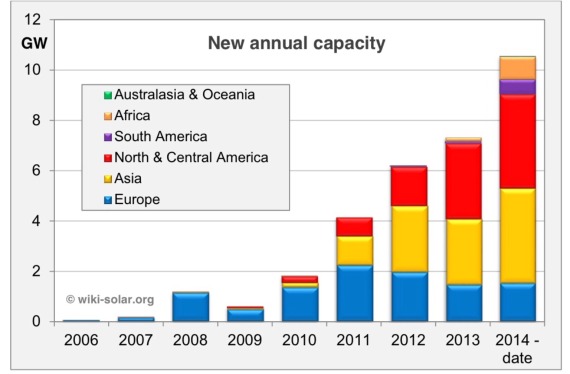
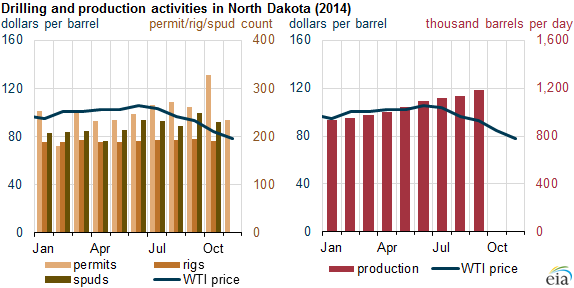

 These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as an open thread. Again I do not want to spend time in comments rehashing whether human activity causes climate change.
These posts are intended to share information and ideas about climate change and hence act as an open thread. Again I do not want to spend time in comments rehashing whether human activity causes climate change.