A miscellany this week, with an emphasis on Australian policy and opinion.
The main links for each item is in the heading.

That’s Millenium Island in Kiribati which tops out at six metres above sea level. In parts of Kiribati the sea level is rising by 1.2 cm a year, about four times more than the global average.
Kiribati recently purchased eight square miles of land about 1,200 miles away on Vanua Levu, Fiji’s second-largest island. The immediate intention relates to food security. They will use the land for agriculture and aquatic farming.
That’s not a lot of land but Kiribati itself comprises just over 100,000 people scattered across 33 low-lying coral atolls totalling about 313 square miles.
The article notes that Kiribati’s reef structure can grow at 10 to 15 mm a year, faster than the IPCC expects sea level to rise, but it is not certain such growth in coral reefs translates to habitable land. My expectation is that later in this century sea level rise will far outstrip any coral growth.
2. Australians unhappy over Coalition’s response to climate challenge
JWS Research on behalf of the Climate Institute found that 70% of Australians accept the mainstream scientific position that climate change is occurring, up 10% since 2012.
while more than half of respondents felt the federal government was the primary body which should address climate change, there was a negative rating of -18 when people were asked to rank the government’s performance.
This compares to a -1 rating from last year.
A mere 20% of those questioned said they are convinced that Tony Abbott is concerned about climate change, with 53% feeling that he isn’t. Nearly a third of people believe opposition leader Bill Shorten is worried about the problem, with around the same proportion of people thinking the reverse is true.
In a further blow to the Coalition, for the first time more people support carbon pricing than oppose it. According to the poll, 34% back the carbon pricing laws, up 6% on 2012. Public opposition to carbon pricing has collapsed by 22% since 2012, when the Coalition was repeatedly attacking the then Labor government over the policy, the poll found.
According to the poll, 47% of people think that carbon pricing is preferable to no climate change policy, with just 22% supporting the government’s alternative Direct Action policy…
3. Shorten vows to ‘re-litigate’ case for carbon pricing
He didn’t expect to have to but he’s prepared to argue the case from first principles. He says:
The real test of political leadership is a willingness to build consensus, to earn agreement, not just to yank the bell at the Downton Abbey political college and expect a servant class of obedient Australians to carry out your will.
Meanwhile confusion reigns in the public mind, so I wish Bill the best of luck. Essential Research found:
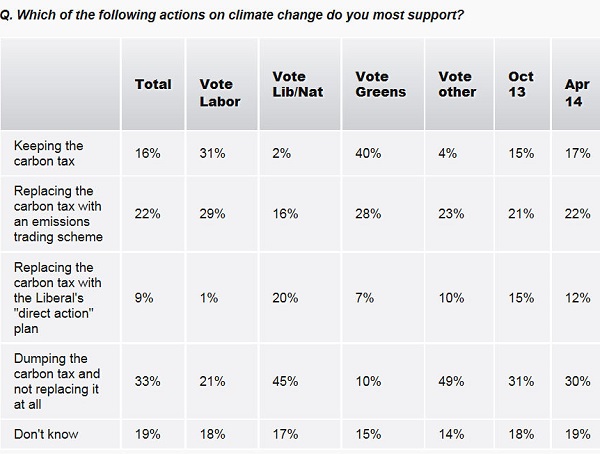
Support for Direct action is thin and fading in this survey at 9%. Doing nothing rates at 33% (up 3%), nearly matching the total of 38% favouring carbon pricing.
4. Great Barrier Reef tougher than thought
Scientists have put together temperatures from the Great Barrier Reef for the last 20,000 years and found that the reef has survived a range of temperatures.
They found that corals survived a 5°C rise between 20,000 years ago and 13,000 years ago. The reef is more resilient to temperature change than previously thought.
Nevertheless there are a few caveat’s to consider before a general outbreak of optimism,
Dr Helen McGregor, a Research Fellow at the Australian National University and a member of the research team:
“The Great Barrier Reef has coped with temperature changes that have occurred over a few thousand years, but now we are looking at a four degrees Celsius temperature change occurring in 100 to 150 years, so it is much more rapid.”
Then there is the small matter of ocean acidification and other human-caused impacts.
5. Abbott slams green power industry
That was the headline on the front page of the Australian Financial Review on Wednesday. On the front page we read the Abbott spiel:
“The RET is very significantly driving up power prices,” Mr Abbott said.
This, he said. posed a threat to domestic budgets and industry competitiveness, especially energy-intensive industries.
“We should be the affordable energy capital of the world, not the unaffordable energy capital of the world and that’s why the carbon tax must go and that’s why we’re reviewing the RET.”
Then over on page four we read the truth:
ACIL modelling for the Warburton review finds keeping the RET will cut average household power bills by $56 per year by 2021-2030 [sic] and extending it to 30 per cent will save householders $158. Source ACIL Allen
Andrew Richards, head of external affairs at Pacific Hydro, said recently approved gas price rises in NSW will add up to $240 a year to the average household bill. There are bigger fish to fry.
It’s a pity that the AFR can’t tell the truth on the front page – that Tony Abbott is telling porkies again.
Reminder: Use this thread as an open thread on climate change.